Probably my favorite subject involving the study of cannabis is The Endocannabinoid System. Have you ever wondered WHY cannabis is so therapeutic for so many medical conditions??? Nobody really understood why until discoveries about the human brain started happening in the 1980s. Thank you, NIDA (National Institute of Drug Abuse) for subsidizing studies leading to breakthroughs about brain chemistry and profound understanding of how the body works and heals. Of course NIDA was designed to prove deleterious effects of cannabis and discredit the use of it for medical use. Teee heee heee
THC was first isolated by Dr. Raphael Mechoulam and T. Gaoni in Israel in 1964 and in the following 20 years, SO much was discovered about the pharmacology, biochemistry and clinical effects of cannabis. The most exciting one being the Endocannabinoid system! Dr. Mechoulam and his colleagues began uncovering this system in 1988. “By using a plant that has been around for thousands of years, we discovered a new physiological system of immense importance,” says Dr. M. “We would not have been able to get there if we had not looked at the plant”.
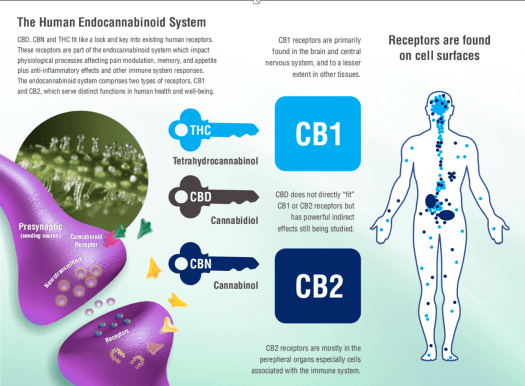
Discovery of cellular membrane cannabinoid receptors occurred in the 1990s, when cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) was found at the synapses of the central nervous system and the sensory neurons’ peripheral terminals. CB 1 receptors are expressed in abundance in the hippocampus, cortex, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and spinal cord. These account for cannabinoid effects on memory, cognition, and movement.
(GW Pharmaceuticals, 2014; Sulak, 2015a)
CB1 receptors are also sparsely found in peripheral nerves, as well as non-neuronal tissue like fat, muscle, and body organs.
Cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2) was found a few years later, predominantly in the immune system and its related structures. CB2 receptors are also present in the gut, spleen, liver, heart, kidneys, bones, blood vessels, lymph cells, endocrine glands and reproductive organs.
Marijuana does so much and is such a versatile medicine because it acts everywhere, not just the brain.
In 1992, Dr. M and his colleagues found another neurotransmitter, a naturally occurring ‘endocannabinoid’ which attaches to the same brain cell receptors as THC. They named it ‘anandamide’ (Sanskrit word for bliss).
In 1995, they discovered a second major endocannabinoid: 2-arachidonoylglyceraol or “2-AG” that locks on to both the CB1 and CB2 receptors. These are the physiological ligands that the body produces for the endocannabinoid receptors, and they create similar effects to cannabis in the body.
****Ligands are small signaling or messaging molecules that bind to the ECS receptor: including human and animal endogenous production of endocannabinoids (anandamide and 2-AG), phytocannabinoids (from plant sources), and synthetic cannabinoids (manufactured) (GW Pharmaceuticals, 2014).
The ECS has many functions in the body and is primarily responsible for managing homeostasis in the body. It helps to manage the central and peripheral nervous systems and impacts physiology in areas such as energy uptake, immune response, storage, reproduction and cellular lifespan.
Cannabinoids help create balance via: Inhibition and excitation of the nervous system, bone formation and resorption, inflammatory/ anti-inflammatory signaling, fat storage and release, and supporting the management of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and hormone levels. (Vipperman, 2014)
Phytocannabinoids (cannabis) and synthetic cannabinoids (dronabinol and nabilone) are known as exocannabinoids.
There are MANY cannabinoids in cannabis, though most often discussed are THC and CBD.
**THC generally works as a cannabinoid receptor agonist at CB1 and CB2 receptor sites; CBD meanwhile works as an antagonist of CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Cannabis has many chemicals that work together to create different effects versus any one chemical alone.
The effects of cannabis have drawn scientists to the still unfolding story of the ECS, which has only recently begun to reveal its profound mysteries. Endocannabinoids and their receptors are a hot topic among scientists and researchers that share their findings in papers and journals hosted by the International Cannabinoid Research Society (ICRS), formed in 1992. For Big Pharma this research is certainly a threat as advances in the cannabinoid studies lead to new treatment strategies for things like diabetes, neuropathic pain, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, etc. Watch out, Big Pharma. RAR.
I find it amazing that the discovery of such an important system was stumbled upon after tracing the metabolic pathways of THC. It seems like cannabis is leading us down a long journey of new information about how our bodies function. It’s amazing…..right??


